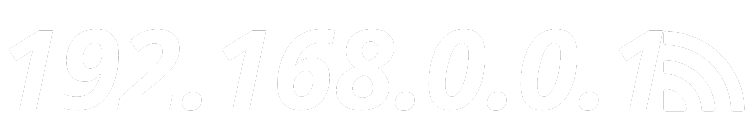When you’re fiddling with setting up your home or office network, the first step to managing all of your router’s functions is logging in. The most common IP address used for this purpose is 192.168.1.1.
Contents
- What is 192.168.1.1?
- How to Access the 192.168.1.1 Admin Page
- Troubleshooting Login Issues
- Configuring Your Router Settings
- Advanced Router Features & Security
- Conclusion
- What is 192.168.1.1?
- What if I Forget My Admin Login Details?
- How Do I Reset My Router to Factory Settings?
- What’s the Difference Between a Default Gateway IP Address and a Router IP Address?
- Why Can’t I Access 192.168.1.1 on My Wi-Fi Connection?
- Is it possible to change the address 192.168.1.1 to another address?
What is 192.168.1.1?

192.168.1.1 is a private IP address used by many routers. It is the default address to log into the router’s administration interface. Private IPs like 192.168.1.1 are used in local networks and are not accessible from the internet.
Difference Between Public Addresses and Private Networks
Public IP addresses are assigned by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). This is a unique address assigned to each device to serve the purpose of connecting to the Internet globally. Each device has only one Public IP address on the Internet for communication. Unlike public IP addresses, private IP addresses are used for communication within the internal network and are not used outside the Internet.

Role of 192.168.1.1 in Home and Office Networks
In your home or office network, 192.168.1.1 serves as the address to set up your router settings. When you enter this address into your web browser, you are taken to the router’s admin access page interface.
Here you can customize your desired network configurations such as changing the network name, changing the password, monitoring children, managing priority devices, etc.
How to Access the 192.168.1.1 Admin Page
Preparations before logging in
- Ensure a stable Internet connection
Check that your device is connected to the router via Wi-Fi or Ethernet cable.
- Verify the Router’s IP Address
Recheck the router’s IP address to make sure you entered the correct address. Be careful not to confuse the IP 192.168.1.1 with 192.168.l.l (where the letter “l” is mistakenly used instead of the number “1”). - Check Connection via Wired or Wireless Network
If using a Wifi network, make sure to select the correct wi-fi network from the router or use an Ethernet cable for a more stable connection.
Four Steps to Login
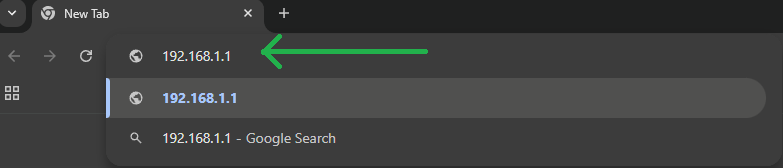
- On your computer or mobile device, open your web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, etc.).
- Type 192.168.1.1 into the browser’s address bar and hit Enter.

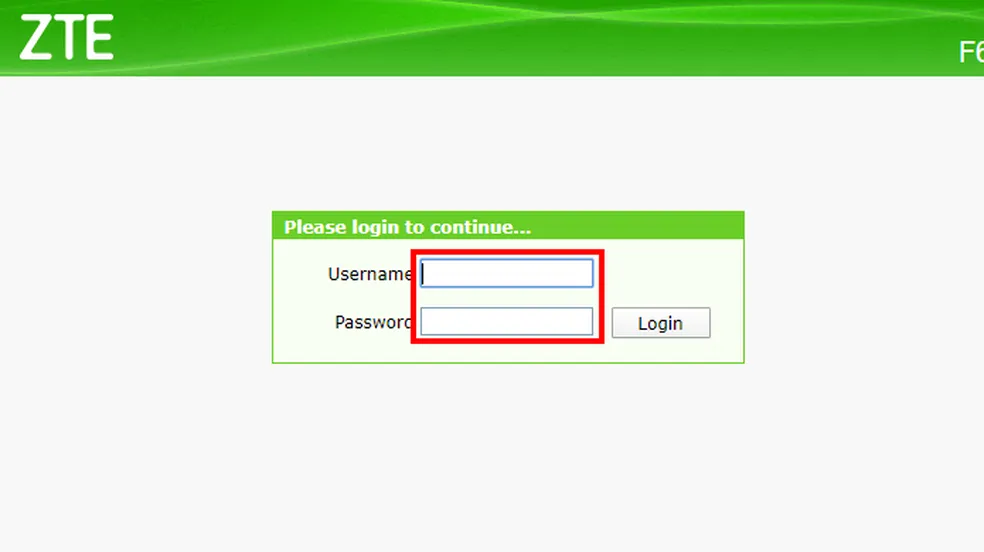
- You’ll be prompted to enter a username and password. The default login credentials are often found on the back of the router or in the router’s user manual.

- Once you have successfully entered your login information, you will be redirected to the router’s admin page, where you can configure custom network settings.
Troubleshooting Login Issues
Can’t Access 192.168.1.1? Common Error Messages and Solutions
If you encounter issues while trying to access 192.168.1.1, try the following:
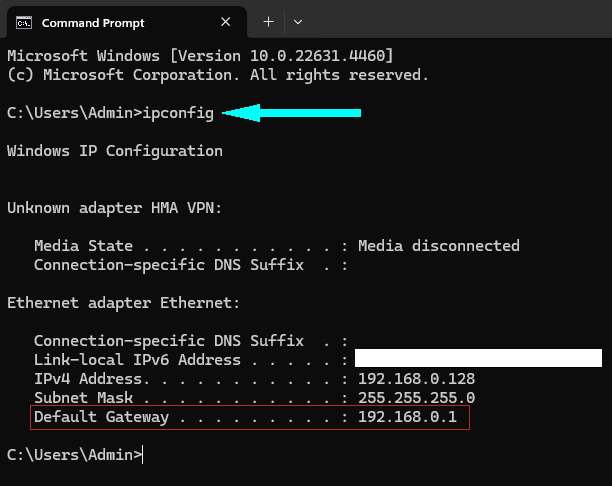
- Check the Default Gateway IP Address
On most versions (Windows 7, Windows 10, Windows 11, etc.), you can find the default gateway IP address by going to the Command Prompt and typingipconfig. This will display the essential IP addresses, including the default gateway.
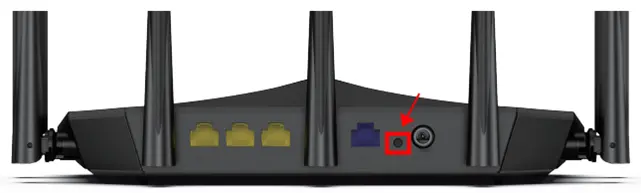
- Reset the Router Settings
If you’ve changed and forgotten your login information or can’t access the admin page, you can reset your router to factory settings using the reset button on the back of the router. Press and hold the button for about 10-15 seconds, then try logging in again with the default credentials.
Configuring Your Router Settings
Change Wi-Fi Network Name & Password
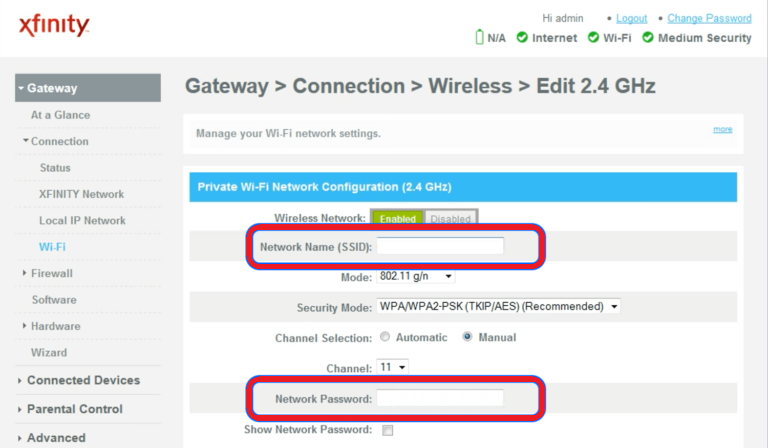
- Navigate to Network Settings → Wi-Fi Settings
Once logged in, go to Wi-Fi settings, however on some router models it may be Wireless Settings, here you can change the network name (SSID) and password.
- Set a Strong Password
To prevent unauthorized users from accessing your network or using tricks to guess your password, set a strong password using a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols - Secure the Network
Enable WPA2/WPA3 encryption to optimize network security against outside intruders.
Manage network settings
- DHCP Server vs. Static IP Configuration
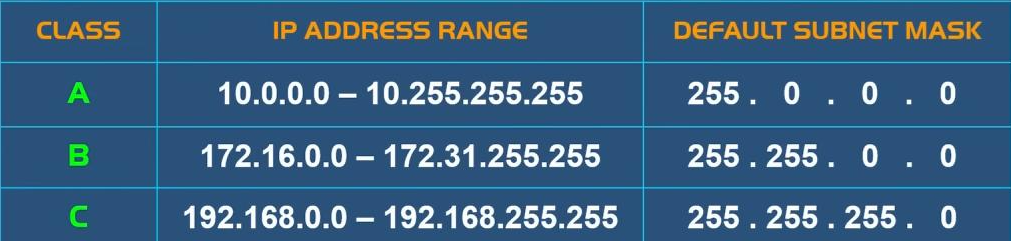
While DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) automatically allocates IP addresses for each device, with Static IP Configuration you will have to manually configure each IP address for each specific device that needs to use the network. - Understanding Subnet Mask and IP Address Ranges
A subnet mask is used to divide a large network into smaller subnets called subnets. Each subnet has its own range of IP addresses. In addition, the address range is made up of a network address and a broadcast address.
- How DHCP Works
DHCP automatically assigns a unique IP address to each device on your network that is connected to your router. This makes it quick and easy to set up addresses automatically instead of manually configuring each address for each device.
Updating Router Firmware
- Keep Your Router’s Firmware Up to Date
Regularly updating your router’s firmware ensures that your device is running the latest security patches and performance improvements. - Where to Find the Latest Firmware
Identify the manufacturer and model of the router you are using. This information is usually printed on a sticker on the bottom or back of the router. You should be able to find the latest firmware version for your router on the manufacturer’s website.
Some popular support sites include:
TP-Link Router: https://www.tp-link.com/en/support/download/
Huawei Router: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/category/routers-pid-1482607112869?submodel=software
Netgear Router: https://www.netgear.com/support/download/
Linksys Router: https://support.linksys.com/home/ - Steps to Update Router Firmware
After downloading the manufacturer’s firmware update, you will log into your router’s control panel. Then look for the firmware update section, each router’s interface is different but you will find the firmware update section under System Tools or Administration. Once you reach the update interface you will see the option to upload a new firmware file. Click on the “Choose File” button and proceed to add the downloaded firmware. To finish, simply click on the “Update” or “Upgrade” button to start the process.
Advanced Router Features & Security
Enabling Network Address Translation (NAT) & Firewall
What is NAT?
Network Address Translation (NAT) allows multiple devices using the same local network to share a single public IP address when accessing the Internet.
Configuring the Router’s Firewall
Depending on your router, you may have the following options:
- Allow or block packets sent based on sending and receiving IP addresses, communication ports, protocols.
- Block specific IP addresses from accessing.
- Block specific domain names such as malicious websites, porn, etc.
- Disallow the router from responding to requests from the internet through network stealth mode.
- Prevent denial of service attacks from overloading your network.
- Set up rules to allow or block specific applications, services, ports.
Setting Up an Access Point
Convert Your Router into an Access Point
You can use your router as an access point to increase your coverage by turning it into a “wi-fi extender”. If your router can support access point(AP) mode.
Note: Not all routers have Access Point mode.
Configure WAN and Ethernet Ports
WAN port is the port that connects your LAN to the Internet. It receives Internet signals from the modem provided by the network operator (fiber optic, ADSL, …) or from the ISP service provider and distributes them to the devices in the LAN.
Ethernet port is used to connect internal devices together, such as computers, laptops, TVs, printers, … connections via Ethernet ports.
Properly configuring the WAN port and ethernet ports allows for smoother internet access and better device management within your network.
Conclusion
192.168.1.1 address is a common access address for many router models, understanding this address makes it easy to manipulate custom configurations as desired. From updating the firmware to securing the Wi-Fi network and preventing unauthorized access, this IP helps quickly identify the causes of your network errors.
What if I Forget My Admin Login Details?
If you forget your login credentials, you can reset the router to factory settings using the reset button.
How Do I Reset My Router to Factory Settings?
Press and hold the reset button for about 10-15 seconds to restore factory settings.
What’s the Difference Between a Default Gateway IP Address and a Router IP Address?
The default gateway IP address routes traffic between different networks, while the router IP address is used to access the router’s admin page.
Why Can’t I Access 192.168.1.1 on My Wi-Fi Connection?
This could be due to incorrect IP address entry, issues with your Wi-Fi connection, or a malfunctioning router.
Is it possible to change the address 192.168.1.1 to another address?
Yes, you can absolutely assign an alternate address to your modem or router if you have more than one device.