Accessing Your ZTE Router: A Comprehensive Guide to Login and Network Configuration
ZTE Router Login is the crucial first step to managing your home network. Whether you need to change your Wi-Fi password, adjust security settings, or troubleshoot connection issues, understanding how to access your router’s administration panel is paramount. Have you ever struggled to find the right login credentials or navigate the interface?
This guide provides a detailed walkthrough of the ZTE Router Login process, covering everything from locating your router’s IP address and default login credentials (often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) to navigating the admin interface and configuring key network settings. We’ll delve into troubleshooting common login problems, exploring solutions for forgotten passwords and network connectivity issues. Finally, we’ll explain how to optimize your network performance for speed and security, leveraging your ZTE router‘s advanced features. Our aim is to empower you with the knowledge to effectively manage your home network and resolve common issues. Understanding your ZTE router‘s capabilities will significantly enhance your online experience.
Contents
- Understanding Your ZTE Router Model and Default Credentials
- Accessing Your ZTE Router via Web Interface
- Common ZTE Router Login Problems and Solutions
- Securing Your ZTE Router After Login
- Advanced ZTE Router Configuration (Optional)
- Troubleshooting Advanced ZTE Router Issues
- Resources and Further Support for ZTE Router Login
Understanding Your ZTE Router Model and Default Credentials
Finding your ZTE router’s model number and default login credentials is the first crucial step in accessing and managing your home network. Knowing this information allows you to configure your router’s settings, troubleshoot network problems, and enhance your network security. This section details how to identify your router’s model and locate the default username and password.
Identifying your ZTE Router Model Number is straightforward, but there are several places to check. The most common location is a sticker on the router itself. This sticker usually contains the model number, serial number, and sometimes even the default Wi-Fi password. Look closely at the back or bottom of your ZTE router. The model number will typically be alphanumeric (e.g., ZTE ZXHN H108N, ZTE MF286D). If you can’t find it physically, you can also attempt to find it through your router’s web interface (once you’ve logged in – instructions are in the following sections). Another useful place to check is the original packaging or your purchase receipt.
Locating your default username and password requires checking several potential sources. The most common approach is to check the label on your router, as mentioned above. Many ZTE routers include this information on the sticker alongside the model number. If the sticker is missing or illegible, you can consult the ZTE’s official website for your specific router model. Their support section typically provides user manuals and FAQs that often list the default credentials. Finally, consider searching for the model number online; many user forums and tech websites provide this information if others have encountered the same router.
Troubleshooting issues related to default credentials can be frustrating. If you’ve lost or forgotten your password, most ZTE routers offer a password reset option. This usually involves pressing a reset button on the router for a specific period (consult your manual for precise instructions). Note that resetting your router will erase all custom settings, reverting it to factory defaults, so back up any critical configurations beforehand. Incorrect model identification is another common problem; double-check the model number carefully to ensure you’re using the correct instructions and information. If you are still experiencing difficulty, exploring the official ZTE support website or searching online forums related to ZTE router logins could offer additional solutions from the community.
This understanding of your ZTE router model and default credentials is essential before proceeding to access your router’s web interface. The next section will guide you through the process of accessing your router via the web interface using the credentials you have successfully identified.
Accessing Your ZTE Router via Web Interface
Accessing your ZTE router’s web interface is the first step to managing your home network’s settings. This process allows you to configure your Wi-Fi network, manage connected devices, and adjust various other settings to optimize your internet experience. Understanding how to access this interface is crucial for troubleshooting network problems and ensuring your network’s security.
Connecting Your Computer to Your Router: Before you can access the router’s web interface, your computer needs to be connected to your ZTE router’s network. This can be done either via a wired Ethernet connection or a wireless Wi-Fi connection. A wired connection is generally preferred for its stability and speed, especially during the initial configuration process. Simply connect one end of an Ethernet cable to your computer’s Ethernet port and the other end to a LAN port on your ZTE router. For a wireless connection, ensure your computer is connected to your ZTE router’s Wi-Fi network. The network name (SSID) and password are usually found on a sticker on the router itself.
Opening Your Web Browser and Entering the Router’s IP Address: Once connected, open a web browser on your computer (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, or Safari are all suitable). Next, you need to type the router’s IP address into the address bar. The most common IP addresses for ZTE routers are 192.168.1.1 and 10.0.0.1. However, this can vary depending on your specific router model and network configuration. If you are unsure of your router’s IP address, you can find it through your computer’s network settings. On Windows, you can usually find this by typing “ipconfig” into the command prompt. On macOS, open System Preferences > Network and look for the IPv4 address assigned to your router.
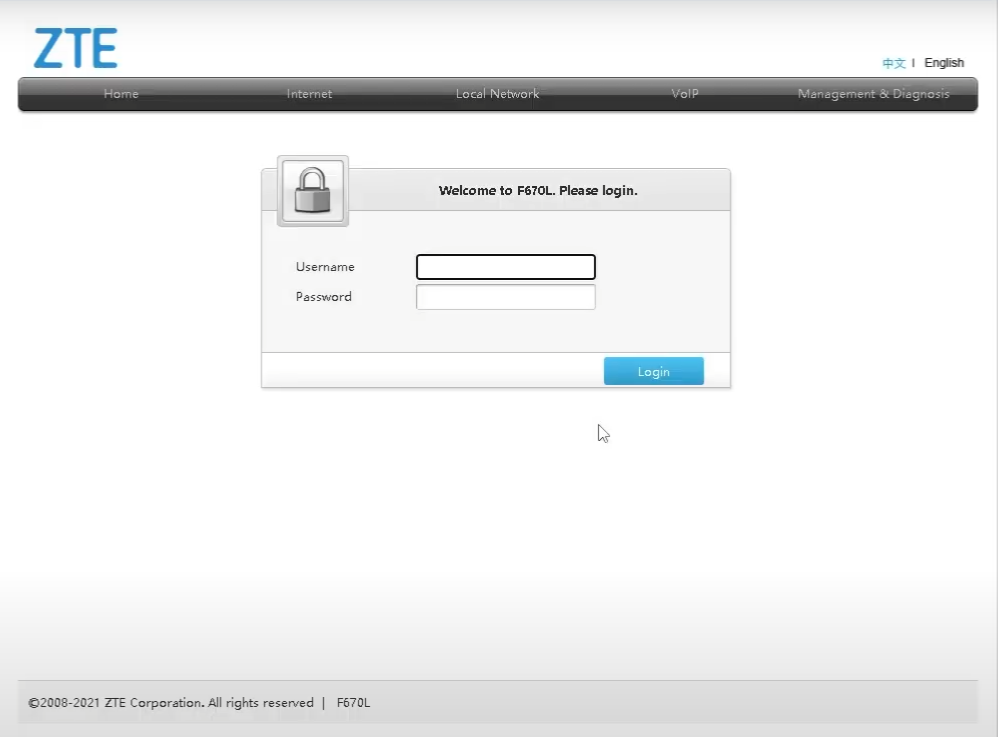
Logging into the Router Using Default Credentials: After entering the IP address and pressing Enter, you will be prompted to log in. The default username and password are usually printed on the router’s label or in the quick start guide. Common defaults include admin/admin, admin/password, or 1234/1234. However, these may differ, so consult your router’s documentation or the label on the device itself.
Troubleshooting Login Issues: If you encounter problems logging in, there are several troubleshooting steps to try:
- Check the IP address: Double-check that you have entered the correct IP address.
- Verify the username and password: Make sure you have entered the correct username and password. Try the common defaults mentioned above. If you’ve changed your password, use the new password.
- Check your network connection: Ensure your computer is correctly connected to the router.
- Restart your router and computer: This can often resolve temporary glitches.
- Consult your router’s documentation: Your router’s manual will provide specific login instructions and troubleshooting tips.
- Reset your router to factory defaults (as a last resort): This will erase all your custom settings, so only do this if you’re comfortable with setting up your router from scratch. The reset button is usually a small, recessed button on the router’s back or bottom.
Successfully logging into your ZTE router’s web interface grants you access to a wide array of configuration options. Remember to change the default password immediately after logging in for enhanced security, as detailed in the subsequent section. This ensures your network’s protection against unauthorized access.
Common ZTE Router Login Problems and Solutions
Accessing your ZTE router’s administration interface is the first step to managing your home network. However, many users encounter difficulties logging in. This section details common ZTE router login problems and provides practical solutions to get you back online.
Many ZTE router login issues stem from incorrect credentials or network connectivity problems. Successfully logging in requires the correct username and password, a stable network connection, and a compatible web browser. Let’s explore these potential roadblocks and how to overcome them.
Incorrect Username or Password: The Most Common Culprit
The most frequent cause of ZTE router login failure is entering the wrong username or password. ZTE routers often employ default credentials, which are frequently listed on a sticker affixed to the router itself or in the user manual. However, these default credentials may have been changed.
- Solution 1: Locate Default Credentials: Check your router’s physical label for the default username and password. Common default usernames include “admin,” while passwords often consist of “admin,” “password,” or a series of numbers. The user manual, accessible via the official ZTE website, provides this information for various router models.
- Solution 2: Reset the Router: If you’ve forgotten your password and cannot locate the default credentials, resetting your router to its factory settings is often the best course of action. This can usually be done by pressing and holding the reset button (often a small pinhole on the back of the router) for 10-30 seconds. This action will erase all custom settings, so ensure you back up important configurations if possible before proceeding. After resetting, use the default credentials to log in.
- Solution 3: Password Recovery (if applicable): Some advanced ZTE router models might offer password recovery features through email or a security question. Check your router’s user manual to see if this option exists.
Network Connectivity Issues: Checking the Basics
Before blaming your credentials, ensure your computer or device has a proper connection to the ZTE router.
- Solution 1: Verify Cable Connections: If using an Ethernet cable, check both ends – the connection to your computer and the connection to the router – to ensure they are securely plugged in. Inspect the cables for any visible damage.
- Solution 2: Check Wireless Signal Strength: If connecting wirelessly, ensure you’re within the router’s range and that the signal strength is adequate. Obstacles like walls, furniture, and electronic devices can interfere with the signal. Consider repositioning your router or connecting with a wired connection for stronger stability.
Browser Compatibility and Troubleshooting
Occasionally, browser incompatibility can hinder your login attempt.
- Solution 1: Try a Different Browser: Try using a different web browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox, Edge) to eliminate browser-related issues. Some older browsers may not be compatible with the router’s interface.
- Solution 2: Clear Browser Cache and Cookies: Clearing your browser’s cache and cookies can sometimes resolve login problems caused by outdated or corrupted data. Check your browser’s settings for instructions on how to clear cache and cookies.
IP Address Conflicts and Double NAT Issues
Less common but still possible, IP address conflicts or Double NAT (Network Address Translation) can block access to your router’s admin page.
- Solution 1: Check for IP Address Duplicates: If you are using devices with static IP addresses on your local network, ensure that these addresses don’t clash with the router’s IP or other devices’ IP addresses. Your router’s manual will list the default IP address (often 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Solution 2: Contact your ISP: If you suspect a Double NAT issue (where your ISP’s router performs NAT in addition to your ZTE router), contacting your internet service provider (ISP) is crucial. They may need to adjust your network configuration.
By systematically addressing these common issues, you significantly improve your chances of successfully logging into your ZTE router and managing your home network effectively. Remember to consult your router’s manual for specific details and model-specific instructions.
Securing Your ZTE Router After Login
Successfully logging into your ZTE router is only the first step; securing it is crucial. Failing to properly secure your router leaves your network vulnerable to unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats. This section details essential steps to safeguard your home network after accessing your ZTE router’s administration interface.
Changing Your Default Password: A Foundation of Router Security
The most critical step after logging in is to change the default password. ZTE routers, like many others, ship with a pre-set password. These defaults are readily available online, making your network an easy target for malicious actors. Replacing this with a strong, unique password is paramount. A strong password should be at least 12 characters long, incorporating uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information like birthdays or pet names. Consider using a password manager to generate and securely store complex passwords. Example of a strong password: P@$$wOrd123!@#.
Enabling the Firewall: Your First Line of Defense
Your ZTE router’s built-in firewall acts as a crucial barrier against unauthorized access attempts. Enabling the firewall is highly recommended, and often enabled by default. However, it’s essential to review the firewall settings to ensure they’re configured optimally. Look for options to block incoming connections from untrusted sources and enable features like intrusion detection or prevention. Most ZTE router interfaces offer intuitive graphical interfaces for firewall management, guiding you through the setup process. Note: While firewalls are effective, they are not foolproof and should be used in conjunction with other security measures.
Securing Your Wireless Network: Choosing the Right Encryption
Your Wi-Fi network is the most accessible entry point to your home network. Using robust encryption is non-negotiable. ZTE routers support various Wi-Fi security protocols. Avoid using outdated protocols like WEP or WPA, as they are easily cracked. Instead, choose WPA2 or, preferably, WPA3, the latest security standard offering significantly enhanced protection against unauthorized access. The process of enabling and configuring WPA2/WPA3 is usually straightforward within the router’s settings. Remember to change the default network name (SSID) to something less obvious than the default name provided by ZTE.
Regular Firmware Updates: Patching Security Vulnerabilities
Outdated firmware can leave your router susceptible to known security vulnerabilities. Regularly checking for and installing firmware updates is essential for maintaining a secure network. ZTE regularly releases firmware updates that address security flaws and improve performance. The process of updating the firmware varies slightly depending on the ZTE router model. Check your router’s documentation or the official ZTE website for specific instructions on updating your router’s firmware. Expect to see a section clearly labeled “Firmware Update” or “System Upgrade” within your router’s administration interface.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Security Measures
While the above steps address the core security aspects, you might consider further enhancements:
- Enable MAC Address Filtering: This allows you to restrict network access to only devices with specific MAC addresses, adding an extra layer of security.
- Disable WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup): WPS is often a target for attacks. Disabling it reduces the attack surface.
- Regularly Review Your Router’s Logs: Monitoring the router’s logs can reveal suspicious activity that may indicate a security breach.
By meticulously following these steps, you significantly enhance your ZTE router’s security, protecting your home network and personal data from potential threats. Remember to consult your router’s manual for specific instructions and configurations. The next section will cover more advanced ZTE router configurations.
Advanced ZTE Router Configuration (Optional)
This section details advanced configuration options for your ZTE router, allowing you to optimize your network performance and security. These settings are optional but can significantly enhance your internet experience. Understanding these features can help you troubleshoot common networking problems and fully utilize your router’s capabilities. Improper configuration may lead to network instability; therefore, proceed with caution and consult your router’s manual if needed.
Port Forwarding and Port Triggering: This feature allows you to forward specific incoming internet traffic to a device on your internal network. This is essential for online gaming, hosting servers, or using applications requiring direct access through specific ports. For instance, if you’re playing an online game that uses port 27015, port forwarding ensures that incoming traffic on that port reaches your gaming PC. Port triggering works similarly, but automatically opens the port only when a device requests an outgoing connection on that port. Incorrectly configuring these settings can compromise your network security, so familiarize yourself with the process before proceeding. Remember to specify the correct internal IP address and port number for the target device.
Guest Network Setup: Creating a separate guest network is vital for enhanced security and network management. A guest network isolates your primary network’s devices and data from guest devices, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information. Setting this up involves creating a new Wi-Fi network with its own unique SSID (network name) and password. You can configure separate security settings and bandwidth limits for the guest network, ensuring your primary network remains secure even with multiple guest devices connected. This is crucial for protecting your privacy and preventing the spread of malware. Consider using a strong, unique password different from your main network password.
Quality of Service (QoS) Settings: QoS allows you to prioritize network traffic for specific applications or devices. This feature is especially beneficial when multiple devices are competing for bandwidth. For example, you can prioritize video streaming over file downloads to ensure smoother video playback. You can usually allocate bandwidth percentage to different devices or application types. Improper QoS configuration may not significantly improve performance and might even introduce network instability, so approach this section carefully. Always consult your router’s manual for specific instructions on setting up QoS for your ZTE router model.
Parental Controls: Many ZTE routers offer robust parental controls, allowing you to restrict internet access for certain devices or during specific time periods. This enables you to filter inappropriate content and set time limits for children’s internet usage. This helps in creating a safe online environment. You can block websites, manage internet access schedules, and even set usage limits for specific devices. Effectively using these tools requires regularly reviewing and updating the controls as your children’s needs and online behaviors evolve.
Understanding and Managing Bandwidth Allocation: Your ZTE router manages how internet bandwidth is distributed across your connected devices. You can monitor bandwidth usage, identify devices consuming excessive bandwidth, and adjust settings to optimize performance. By understanding your network’s usage pattern, you can effectively allocate bandwidth based on priority needs. This might involve reducing bandwidth for less critical applications during peak usage times or temporarily limiting a device’s access to improve overall network speed. This feature requires a deeper understanding of network protocols and your individual network’s usage patterns. Regular monitoring of bandwidth allocation can help identify bottlenecks and optimize your network’s performance.
This concludes the advanced configuration options for your ZTE router. While optional, mastering these features significantly enhances network control, security, and overall user experience. Remember to consult your router’s manual for model-specific instructions and always back up your current settings before making significant changes. By utilizing these advanced settings, you can transform your home network from a simple connection point to a finely tuned and secure system.
Troubleshooting Advanced ZTE Router Issues
Slow Internet Speeds: Identifying and Resolving Performance Bottlenecks
Experiencing sluggish internet speeds despite a strong ZTE router login? This isn’t just about a weak signal; it points to deeper network issues. Several factors can contribute to slowdowns, affecting your overall online experience. Understanding these factors is key to effectively troubleshooting and resolving the problem. Addressing these issues often involves a combination of checks and adjustments, from simple solutions to more advanced configurations.
- ISP Connection Issues: The first step involves checking the connection with your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Are you receiving the speeds you’re paying for? A speed test (using a reputable site like Ookla’s Speedtest.net) provides a baseline. Contact your ISP if the results are significantly below your plan’s advertised speed. This could indicate problems on their end, such as network congestion or outages. The ISP‘s status page often provides information on current service interruptions.
- Router Placement and Interference: Optimizing your ZTE router’s physical location can dramatically improve performance. Avoid placing it near microwave ovens, cordless phones, or other devices that operate on the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz frequencies. These sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI) can significantly weaken the WiFi signal. Ideal placement is centrally located and elevated for optimal signal distribution. Consider the materials your router sits on; metal surfaces can impede signal strength.
- Wired vs. Wireless Connection: While wireless is convenient, wired connections via Ethernet cables always offer significantly faster and more stable speeds. If your devices allow, connecting directly to your router via Ethernet often eliminates wireless interference as a potential cause of slowdowns. Compare speeds between wired and wireless connections to isolate the source of the performance issue. Testing this difference can quickly determine if a wireless issue is at play.
- Network Congestion: Multiple devices simultaneously streaming high-bandwidth content (4K video, online gaming) can overwhelm your router’s capacity. Using Quality of Service (QoS) settings within your router’s advanced configuration (detailed in the Advanced ZTE Router Configuration section) allows you to prioritize bandwidth for specific devices or applications. This ensures critical applications get the necessary bandwidth, even during periods of high network activity.
Internet Connectivity Problems: Systematic Diagnostics and Solutions
A complete loss of internet connectivity requires a systematic troubleshooting approach. The issue might lie within your local network configuration or be caused by problems outside your home network. A step-by-step approach increases your chances of resolving the problem quickly and efficiently.
- Cable Connections: Begin by carefully checking all cable connections. Ensure the Ethernet cable connecting your modem to your ZTE router is securely plugged into both devices. Loose connections are a surprisingly common cause of internet outages. Similarly, check all power cables to ensure the router and modem are properly powered on. Visually inspect the cables for any visible damage.
- Router Restarts: A simple router restart often resolves temporary glitches. Unplug your ZTE router’s power cord, wait 30 seconds, then plug it back in. Allow a few minutes for the router to fully boot up and re-establish connections before testing your internet connectivity. If this doesn’t fix the problem, continue to the next steps.
- Modem Issues: If the problem persists after checking your router, the issue might be with your modem. Try restarting your modem using the same method as the router restart. If still no internet, your ISP may be experiencing an outage, or your modem might need replacement.
- Contacting Your ISP: If restarting your router and modem doesn’t solve the connectivity issue, contact your ISP for assistance. They can check for outages in your area or diagnose issues on their end. Provide them with the results of your speed test and any error messages you’ve encountered.
Wireless Connectivity Issues: Optimizing Signal Strength and Eliminating Interference
Wireless connectivity problems often manifest as intermittent connection drops, slow speeds, or an inability to connect to the network altogether. Troubleshooting these problems involves carefully examining signal strength, interference, and channel selection.
- Signal Strength: The strength of your WiFi signal significantly affects performance. Using your router’s management interface, check the signal strength reported for each connected device. Weak signals necessitate moving the router closer to the devices or employing WiFi extenders/mesh networks to improve coverage. The ideal signal strength should be above 70% for optimal performance.
- Interference: As mentioned earlier, appliances operating on similar frequencies can interfere with your WiFi signal. Identify potential sources of interference (EMI) and relocate your router or the devices to minimize signal disruption. Experimenting with different channels can help mitigate the impact of overlapping signals from neighboring WiFi networks. Most routers allow you to select a different WiFi channel in the advanced settings.
- Channel Selection: Using a WiFi analyzer app (available for smartphones and computers), identify less congested WiFi channels in your area. Adjust your ZTE router’s channel settings to one with minimal interference. This often leads to a significant improvement in connection stability and speed. Avoid channels 1, 6, and 11 if possible, as they are often heavily used.
Specific Error Messages: Decoding and Addressing ZTE Router Error Codes
Encountering specific error messages on your ZTE router’s interface, or even on your connected devices, can pinpoint the problem’s origin. These codes often provide clues to understanding the root cause of the issue.
- Documentation and Online Resources: Consult your ZTE router’s manual, the official ZTE support website, or online forums for information on specific error codes. The manual often provides a detailed list of error codes and their corresponding meanings, enabling you to quickly identify and address the cause. Use the exact error message in your online searches.
- Troubleshooting Steps: Based on the error message, follow the specific troubleshooting steps recommended in your router’s documentation or online resources. These may involve changing specific settings, restarting your router, or contacting ZTE support.
By systematically following these troubleshooting steps, you can efficiently identify and resolve various advanced ZTE router issues, ensuring optimal network performance and connectivity. Remember to consult your router’s user manual and utilize online resources for more specific guidance related to your ZTE router model. Understanding and leveraging the advanced configuration options of your ZTE router can also dramatically improve its performance.
Resources and Further Support for ZTE Router Login
Finding yourself stuck with your ZTE router login? Don’t worry, you’re not alone. Many users encounter challenges accessing their router’s administration interface. This section provides valuable resources and support options to help you resolve login issues and get the most out of your ZTE router. We’ll cover official support channels, community forums, and troubleshooting guides to ensure you’re back online quickly.
Official ZTE Support Website: Your First Stop for Troubleshooting
The official ZTE support website is your primary resource for resolving ZTE router login problems. This site offers a wealth of information, including:
- Comprehensive user manuals: Detailed guides explaining every aspect of your specific ZTE router model, including login procedures, troubleshooting steps, and advanced configuration options. These manuals often contain diagrams and screenshots to make the process easier.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): A dedicated section addressing common issues, such as forgotten passwords, incorrect login credentials, and network connectivity problems. You’ll find quick solutions to many common problems here, saving you time and effort.
- Troubleshooting guides: Step-by-step instructions for diagnosing and resolving a wide range of router problems, from basic connectivity issues to more advanced configuration errors. These guides often include diagnostic tools and tips to speed up the troubleshooting process.
- Firmware updates: Access to the latest firmware updates for your ZTE router model. Keeping your firmware up-to-date ensures optimal performance, security, and stability, minimizing the risk of encountering login problems. Remember, outdated firmware can sometimes lead to login failures. The support website will guide you through the safe and proper updating process.
Accessing the official ZTE support website is the first step in successfully troubleshooting any ZTE router login difficulties. Remember to accurately identify your router model number (often found on a sticker on the router itself) for the most relevant support.
Online Forums and Communities: Connecting with Fellow ZTE Router Users
Engaging with online communities dedicated to ZTE routers can provide valuable insights and solutions. These forums are filled with users who have faced similar challenges and are willing to share their experiences and troubleshooting techniques. Searching for “[your ZTE router model] login problem” or “ZTE router support” on popular online forums like Reddit, Tom’s Hardware, or DSLReports can yield helpful results.
- Shared Knowledge: Forums offer a collective pool of knowledge. Other users might have encountered and solved a problem you’re facing, saving you time and frustration. Learn from the collective wisdom of the community.
- Peer-to-Peer Support: Receive direct support from fellow users who understand the intricacies of ZTE router configurations. This personal interaction often provides faster and more tailored solutions than official support channels.
- Community-Based Troubleshooting: Detailed, step-by-step guidance is often provided in forum discussions. These discussions may walk you through troubleshooting steps not explicitly documented in official manuals.
However, always exercise caution and verify information found in online forums before implementing it. Not all advice may be accurate or applicable to your specific situation.
Contacting ZTE Customer Support: Direct Assistance When Needed
If you’ve exhausted all other options, contacting ZTE customer support directly provides access to expert assistance. Most manufacturers offer multiple contact options, including:
- Phone support: Provides immediate assistance for urgent issues. Expect to provide your router model number and a detailed description of the problem.
- Email support: Suitable for less urgent issues or when detailed information is required. Attaching screenshots or diagnostic logs can help streamline the troubleshooting process.
- Live chat support: Offers a quick and convenient way to ask questions and receive immediate assistance. This is a great option for basic login problems.
Remember to have your router’s model number, serial number, and a clear description of the problem readily available when contacting support. This will speed up the process and allow customer service representatives to assist you effectively.
By utilizing these resources, you can effectively overcome most ZTE router login issues and regain access to your network’s administration interface. Remember to prioritize official support channels first, then leverage community forums and direct customer support as needed.